Internal auditor training on 27001 ISMS, Uncategorized
Internal auditor training on 27001 ISMS
Courtesy: Internal auditor training on 27001 ISMS
ISO framework is a combination of policies and processes for organizations to use. ISO 27001 provides a framework to help organizations, of any size or any industry, to protect their information in a systematic and cost-effective way, through the adoption of an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Why is ISO 27001 important?
Not only does the standard provide companies with the necessary know-how for protecting their most valuable information, but a company can also get certified against ISO 27001 and, in this way, prove to its customers and partners that it safeguards their data.
Individuals can also get ISO 27001-certified by attending a course and passing the exam and, in this way, prove their skills to potential employers.
Because it is an international standard, ISO 27001 is easily recognized all around the world, increasing business opportunities for organizations and professionals.

What are the 3 ISMS security objectives?
The basic goal of ISO 27001 is to protect three aspects of information:
- Confidentiality: only the authorized persons have the right to access information.
- Integrity: only the authorized persons can change the information.
- Availability: the information must be accessible to authorized persons whenever it is needed.
What is an ISMS?
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) is a set of rules that a company needs to establish in order to:
- identify stakeholders and their expectations of the company in terms of information security
- identify which risks exist for the information
- define controls (safeguards) and other mitigation methods to meet the identified expectations and handle risks
- set clear objectives on what needs to be achieved with information security
- implement all the controls and other risk treatment methods
- continuously measure if the implemented controls perform as expected
- make continuous improvement to make the whole ISMS work better
This set of rules can be written down in the form of policies, procedures, and other types of documents, or it can be in the form of established processes and technologies that are not documented. ISO 27001 defines which documents are required, i.e., which must exist at a minimum.
There are four essential business benefits that a company can achieve with the implementation of this information security standard:
Comply with legal requirements – there is an ever-increasing number of laws, regulations, and contractual requirements related to information security, and the good news is that most of them can be resolved by implementing ISO 27001 – this standard gives you the perfect methodology to comply with them all.
Achieve competitive advantage – if your company gets certified and your competitors do not, you may have an advantage over them in the eyes of those customers who are sensitive about keeping their information safe.
Lower costs – the main philosophy of ISO 27001 is to prevent security incidents from happening – and every incident, large or small, costs money. Therefore, by preventing them, your company will save quite a lot of money. And the best thing of all – investment in ISO 27001 is far smaller than the cost savings you’ll achieve.
Better organization – typically, fast-growing companies don’t have the time to stop and define their processes and procedures – as a consequence, very often the employees do not know what needs to be done, when, and by whom. Implementation of ISO 27001 helps resolve such situations, because it encourages companies to write down their main processes (even those that are not security-related), enabling them to reduce lost time by their employees.
How does ISO 27001 work?
The focus of ISO 27001 is to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the information in a company. This is done by finding out what potential problems could happen to the information (i.e., risk assessment), and then defining what needs to be done to prevent such problems from happening (i.e., risk mitigation or risk treatment).
Therefore, the main philosophy of ISO 27001 is based on a process for managing risks: find out where the risks are, and then systematically treat them, through the implementation of security controls (or safeguards).
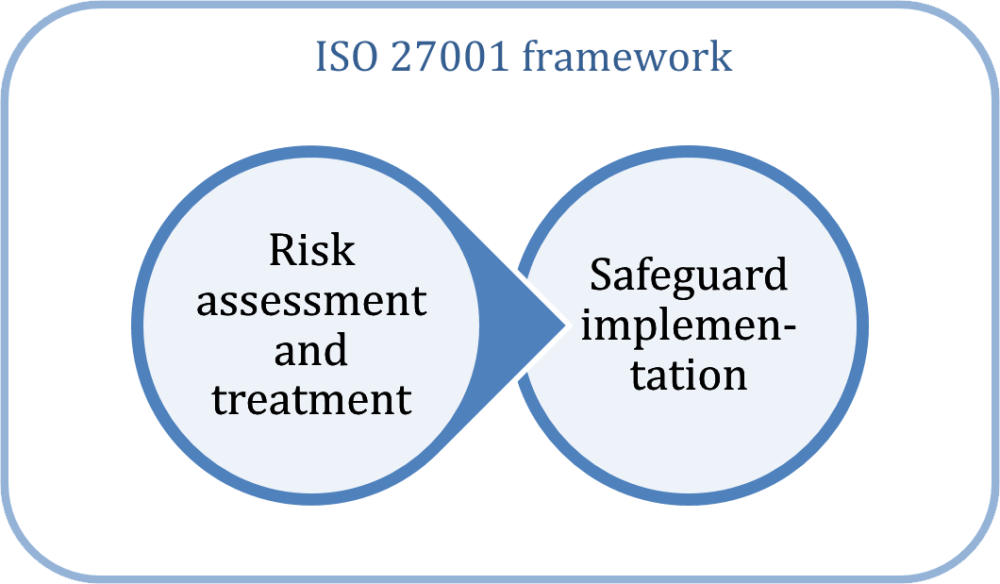
ISO 27001 requires a company to list all controls that are to be implemented in a document called the Statement of Applicability.
Two parts of the standard
The standard is separated into two parts. The first, main part consists of 11 clauses (0 to 10). The second part, called Annex A, provides a guideline for 114 control objectives and controls. Clauses 0 to 3 (Introduction, Scope, Normative references, Terms and definitions) set the introduction of the ISO 27001 standard. The following clauses 4 to 10, which provide ISO 27001 requirements that are mandatory if the company wants to be compliant with the standard, are examined in more detail further in this article.
Annex A of the standard supports the clauses and their requirements with a list of controls that are not mandatory, but that are selected as part of the risk management process. For more, read the article
REQUIREMENTS & SECURITY CONTROLS
What are the requirements for ISO 27001?
The requirements from sections 4 through 10 can be summarized as follows:
Clause 4: Context of the organization – One prerequisite of implementing an Information Security Management System successfully is understanding the context of the organization. External and internal issues, as well as interested parties, need to be identified and considered. Requirements may include regulatory issues, but they may also go far beyond


