A “disaster”, noun, is defined as a calamitous event, especially one occurring suddenly and causing great loss of life, damage or hardship such as a flood, aircraft crash or an angry person. “Response” is defined (in this context) as: Noun: An answer or reply, as in words or in some action.
The Business Dictionary provide a more comprehensive definition for “disaster response”; Aggregate of decisions and measures to (1) contain or mitigate the effects of a disastrous event to prevent any further loss of life and/or property, (2) restore order in its immediate aftermath, and (3) re-establish normality through reconstruction and re-rehabilitation shortly thereafter. The first and immediate response is called emergency response.
The Johns Hopkins and the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) state: “The word disaster implies a sudden overwhelming and unforeseen event. At the household level, a disaster could result in a major illness, death, a substantial economic or social misfortune. At the community level, it could be a flood, a fire, a collapse of buildings in an earthquake, the destruction of livelihoods, an epidemic or displacement through conflict. When occurring at district or provincial level, a large number of people can be affected.”
A recent case study of a disaster response undertaken by the IFRC can be viewed here.
The level of disaster response depends on a number of factors and particular situation awareness. Studies undertaken by Son, Aziz and Peña-Mora (2007) shows that “initial work demand gradually spreads and increases based on a wide range of variables including scale of disaster, vulnerability of affected area which in turn is affected by population density, site-specific conditions (e.g. exposure to hazardous conditions) and effects of cascading disasters resulting from inter-dependence between elements of critical infrastructure”.
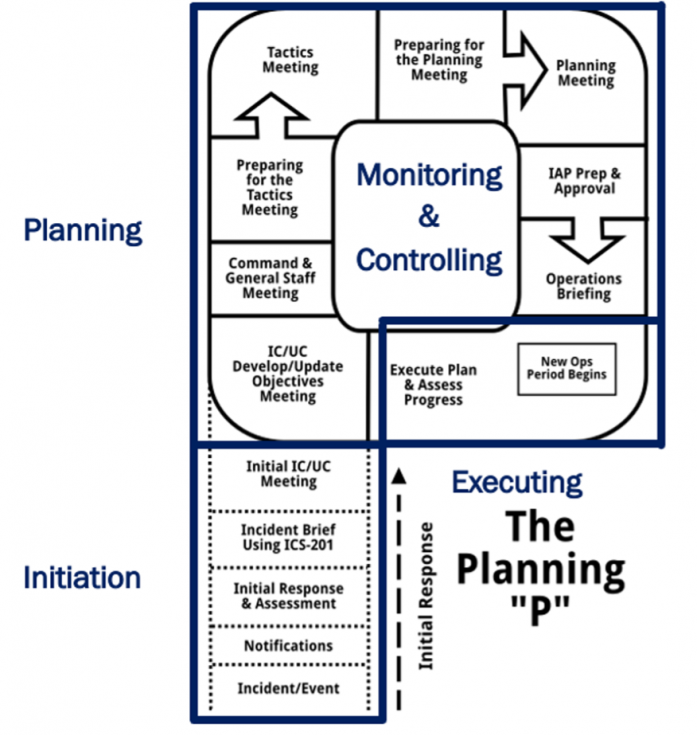
In the British Government’s Emergency Response and Recovery guidance, disaster response refers to decisions and actions taken in accordance with the strategic, tactical and operational objectives defined by emergency responders. At a high level these will be to protect life, contain and mitigate the impacts of the emergency and create the conditions for a return to normality. Response encompasses the decisions and actions taken to deal with the immediate effects of an emergency. In many scenarios it is likely to be relatively short and to last for a matter of hours or days—rapid implementation of arrangements for collaboration, co-ordination and communication are, therefore, vital. Response encompasses the effort to deal not only with the direct effects of the emergency itself (e.g. fighting fires, rescuing individuals) but also the indirect effects (e.g. disruption, media interest).
Common objectives for responders are:
- saving and protecting human life;
- relieving suffering;
- containing the emergency – limiting its escalation or spread and mitigating its impacts;
- providing the public and businesses with warnings, advice and information;
- protecting the health and safety of responding personnel;
- safeguarding the environment;
- as far as reasonably practicable, protecting property;
- maintaining or restoring critical activities;
- maintaining normal services at an appropriate level;
- promoting and facilitating self-help in affected communities;
- facilitating investigations and inquiries (e.g. by preserving the scene and effective records management);
- facilitating the recovery of the community (including the humanitarian assistance, economic, infrastructure and environmental impacts);
- evaluating the response and recovery effort; and
- identifying and taking action to implement lessons identified.